Veterinary Endoscopy
The care your pet deserves
What is Endoscopy?
Endoscopy (minimally invasive surgery)is a technique for performing medical procedures through natural openings in the body or through one or more tiny holes. An endoscope inserted in the body magnifies internal structures on a TV monitor for thorough examination. Surgical instruments may be used through the same opening or through an additional small incision.
By performing procedures endoscopically, vets offer their patients less pain, minimal recovery time and fewer complications. In many cases, performing a procedure endoscopically allows the patient to return home the same day.
Advantages of Endoscopy:
Less pain
Excellent visualization of internal organs
Fewer complications
Faster recovery
Ability to access otherwise inaccessible parts of the body

Applications of Veterinary Endoscopy
Endoscopic techniques have been developed in many areas of veterinary medicine to offer you and your pet less invasive - and less painful - alternatives to traditional open surgery. Some of the most common endoscopic procedures are listed here, but specialists continue to expand the application of endoscopy to other areas. If your pet requires surgery, please discuss with your vet how endoscopy may be the best option.
Arthroscopyis endoscopy of the joint. It is used in cases of chronic lameness, joint pain, joint instability, swelling and abnormal radiographic findings.
Bronchoscopyis endoscopy of the airways and lungs, to identify structural abnormalities, collect samples of abnormal airway secretions, identify and remove foreign bodies and biopsy lesions or masses.
Cystoscopyis endoscopy of the urinary bladder, used in patients presenting with chronic infections, blood in the urine, straining to urinate, incontinence, trauma, stones and abnormal radiographs.
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy is the endoscopic exploration of the stomach and intestines. A partial list of indications includes chronic regurgitation, salivation, nausea, vomiting, blood in the stool, anorexia, diarrhea, weight loss, fecal mucus and straining to defecate. It is most commonly used for obtaining biopsies and the removal of foreign bodies.
Gastropexy is a preventative surgery that can be performed laparoscopically on at-risk dogs to prevent the twisting of the stomach, which is fatal if not treated quickly. The stomach is sutured to the abdominal wall in order to prevent the stomach from twisting. Endoscopy eliminates the need to perform open surgery, which requires an incision of6" to 12". Gastropexy is often done at the time of laparoscopic spay.
Gastropexy is a preventative surgery that can be performed laparoscopically on at-risk dogs to prevent the twisting of the stomach, which is fatal if not treated quickly. The stomach is sutured to the abdominal wall in order to prevent the stomach from twisting. Endoscopy eliminates the need to perform open surgery, which requires an incision of6" to 12". Gastropexy is often done at the time of laparoscopic spay.
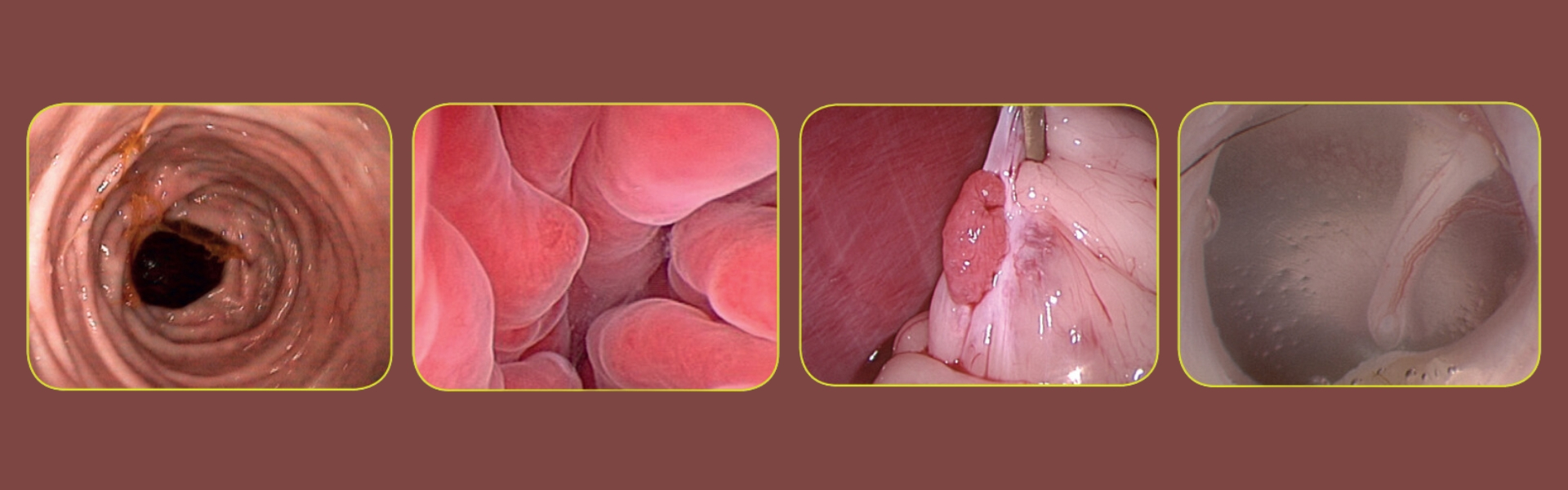
Laparoscopy is endoscopy of the abdominal cavity, used as a diagnostic tool for taking biopsies of the liver, kidney and pancreas. More complex laparoscopic surgeries being performed include adrenalectomy, gastropexy, hernia repair and spays.
Laparoscopic Spay is a technique for neutering female cats and dogs. Performed through one to three small incisions in the abdomen rather than a large incision, it offers a less painful, safer and faster healing alternative to traditional spays.
Otoscopy is endoscopy of the external and middle ear. It is one of the most common applications of endoscopy in veterinary medicine. Otoscopy allows for safe and thorough ear cleaning under constant visualization, removal of foreign objects, polyp removal and diagnostic sampling.
Rhinoscopy is endoscopy of the nasal cavity, commonly indicated in dogs and cats with chronic nasal discharge, nasal obstruction, chronic sneezing, nasal bleeding, facial distortion, nasal pain, acute severe sneezing, reverse sneezing and abnormal radiographs.
Vaginoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the vagina. Indications for vaginoscopy include vaginal discharge, bleeding or masses, trauma, incontinence, foreign body removal and straining to urinate. Reproductive indications include transcervical artificial insemination, difficulty inlabor and monitoring of the estrous cycle.